Collagen Peptides
Collagen is a vital protein that plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure, strength, and elasticity of various tissues in the human body. As the most abundant protein in mammals, collagen accounts for about 30% of the total protein mass. Over the years, collagen peptides—also known as hydrolyzed collagen or collagen hydrolysate—have gained significant attention for their potential health benefits and wide-ranging applications. In this article, we explore collagen peptides, their sources, bioavailability, and the various ways they can positively impact human health.
What Are Collagen Peptides?
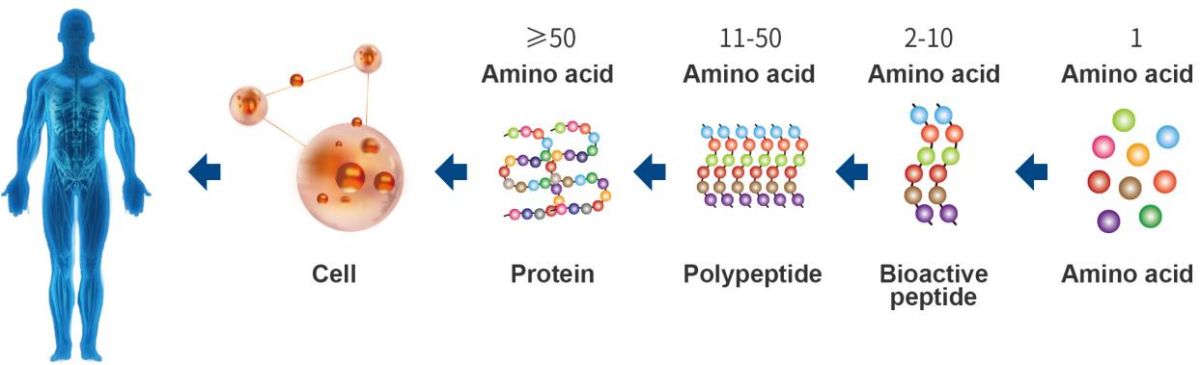
Collagen peptides are derived from collagen through a process known as enzymatic hydrolysis. This process breaks down large collagen molecules into smaller peptides, making them more bioavailable and easily absorbed by the body. The resulting peptides typically contain a mix of amino acids, including glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, which are vital for maintaining the health of connective tissues.
Sources of Collagen Peptides
Collagen peptides can be obtained from various sources, both animal and marine. The most commonly used sources include:
Bovine (Cattle): Known for its high collagen content, particularly in bones and skin.
Porcine (Pigs): Provides a similar amino acid profile to bovine collagen, often used in supplements.
Chicken: Rich in type II collagen, particularly beneficial for joint health.
Fish (Marine Collagen): Derived from fish skin, scales, or bones, and often considered superior due to its higher bioavailability and lower molecular weight.
Each source offers a slightly different amino acid profile, but all provide essential nutrients for improving skin elasticity, joint function, and overall health.
Bioavailability and Absorption
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides have a significantly enhanced bioavailability due to their low molecular weight, which allows for rapid digestion and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, amino acids are efficiently delivered to target tissues like the skin, joints, bones, and other connective tissues. Studies have shown that collagen peptides are readily absorbed and distributed throughout the body, providing specific benefits to each tissue type.
Health Benefits of Collagen Peptides
Skin Health
Collagen peptides have been shown to improve skin health by enhancing hydration, elasticity, and firmness, while also reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Research indicates that collagen supplementation can boost collagen production in the skin, helping to restore its youthful appearance and promote overall skin vitality. For example, Asserin et al. (2015) found positive effects on skin moisture and collagen network structure.
Joint and Bone Health
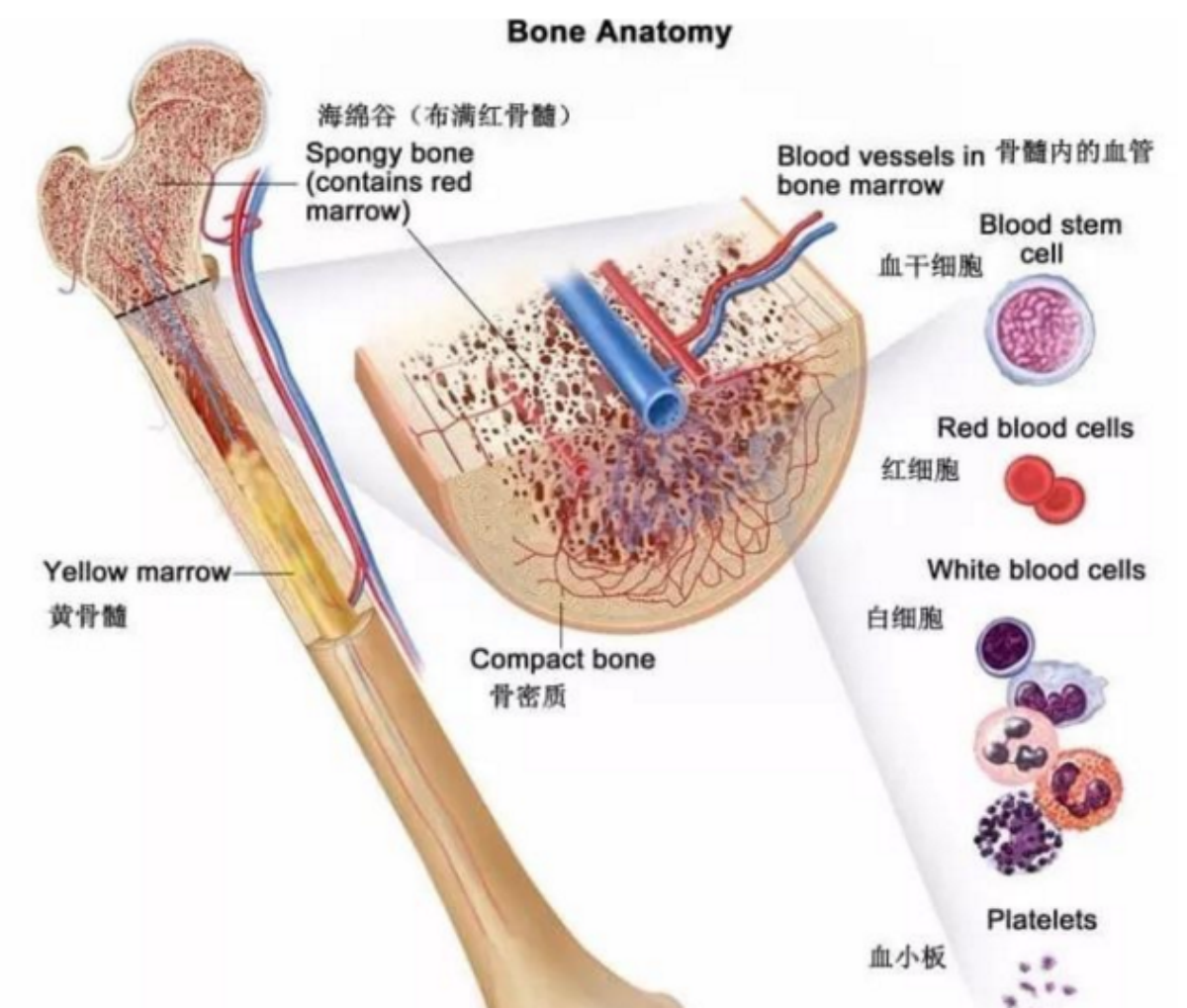
Collagen peptides support joint health by stimulating the production of collagen and proteoglycans in cartilage, which can help alleviate pain and improve mobility in individuals with osteoarthritis. Additionally, collagen peptides contribute to bone health by stimulating osteoblasts (cells responsible for bone formation), leading to stronger bones and reduced risk of fractures. Studies by Bello and Oesser (2006) and Clark et al. (2008) have shown significant benefits of collagen supplementation for joint and bone health.
Sports Performance and Muscle Recovery
Collagen peptides are rich in specific amino acids, such as glycine and proline, which play a vital role in muscle repair and growth. Supplementing with collagen peptides can aid in muscle recovery, reduce exercise-induced joint pain, and enhance athletic performance, making them a popular choice among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. A study by Guillerminet et al. (2012) demonstrated the positive effects of collagen supplementation on bone metabolism, which can be beneficial for athletes.
Gut Health
Collagen peptides, particularly the amino acid glycine, support gut health by strengthening the intestinal lining and promoting proper digestion. They have been linked to improving conditions like leaky gut syndrome and may enhance overall digestive function, helping to maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
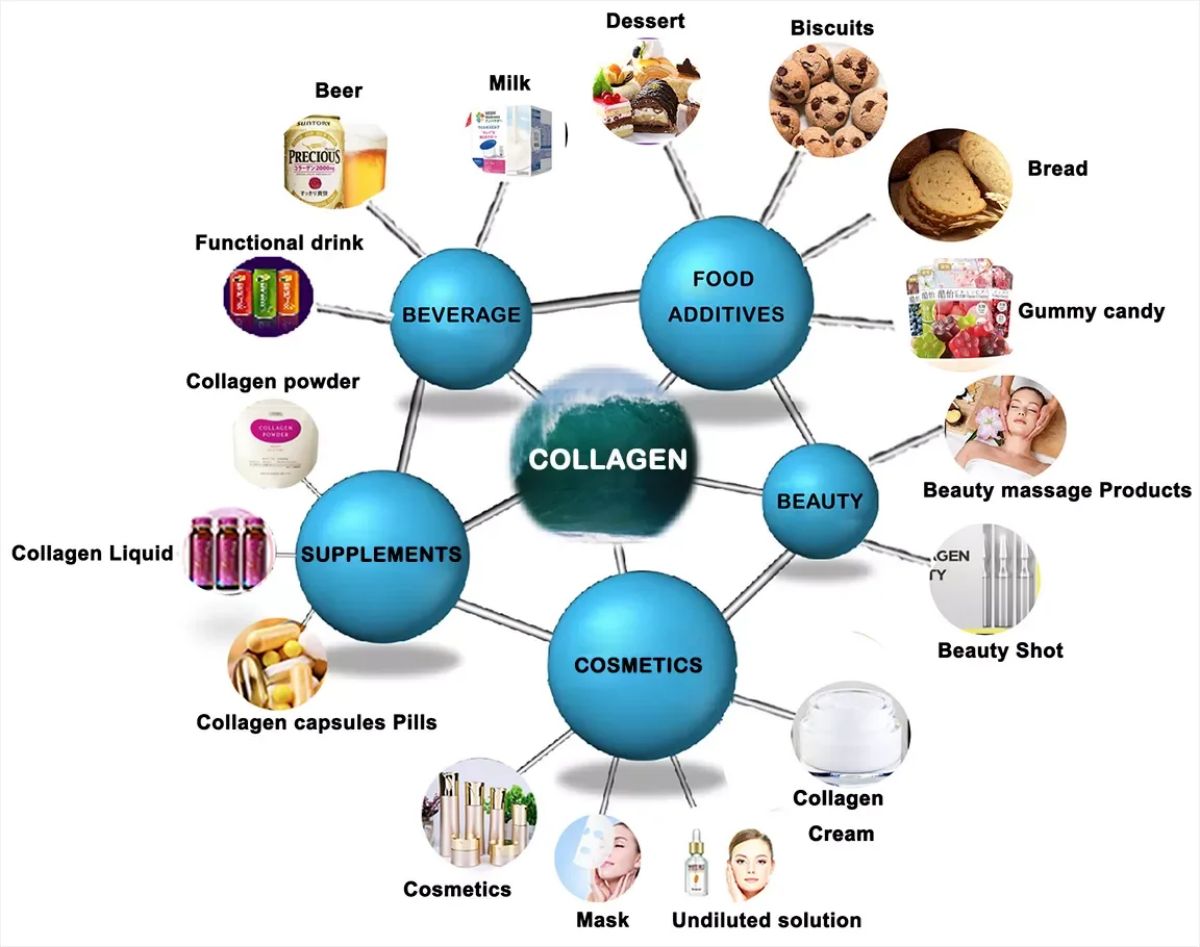
Applications Beyond Health
Collagen peptides are used in various industries, including food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. They are incorporated into protein-rich foods, dietary supplements, and beauty products due to their easy integration, functional benefits, and versatility. Collagen peptides are also being explored for their potential in pharmaceutical formulations aimed at supporting joint health, skin aging, and muscle recovery.
Conclusion
Collagen peptides have emerged as a powerful nutritional supplement with a wide array of health benefits. From promoting skin health and joint function to supporting muscle recovery and enhancing gut health, collagen peptides offer diverse applications for improving overall well-being. Their high bioavailability, specific amino acid composition, and variety of sourcing options make them a versatile ingredient for various health-related purposes. As ongoing research continues to reveal new benefits, collagen peptides hold immense potential for improving human health and quality of life.
References
- Asserin, J., Lati, E., Shioya, T., & Prawitt, J. (2015). The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 14(4), 291-301. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12199
- Bello, A. E., & Oesser, S. (2006). Collagen hydrolysate for the treatment of osteoarthritis and other joint disorders. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 22(11), 2221-2232. https://doi.org/10.1185/030079906X149114
- Clark, K. L., Sebastianelli, W., Flechsenhar, K. R., Aukermann, D. F., Meza, F., Millard, R. L. (2008). 24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 24(5), 1485-1496. https://doi.org/10.1185/030079908X289385
- Guillerminet, F., Fabien-Soulé, V., Even, P. C., & Tomé, D. (2012). Hydrolyzed collagen improves bone metabolism and biomechanical parameters in ovariectomized mice: an in vitro and in vivo study. Bone, 50(3), 876-883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2011.12.032
- Vollmer, D. L., West, V. A., & Lephart, E. D. (2018). Enhancing skin health: by oral administration of natural compounds and minerals with implications to the dermal microbiome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103059
Post time: Dec-25-2024